1. Regulatory Definition & Purpose
The Commercial Invoice is the primary legal instrument used by customs authorities globally to assess import duties, taxes, and admissibility of goods.
Unlike standard accounting invoices, this document functions as a binding declaration to the government of the importing country. It must legally certify the true value, origin, and classification of the merchandise.
2. Document Classification
Strict adherence to the correct document type is required for each stage of the supply chain.
| Document Class | Legal Status | Execution Time | Customs Validity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Commercial Invoice | Final Bill of Sale | At time of Export | Valid & Mandatory |
| Proforma Invoice | Preliminary Quote | Pre-shipment (Negotiation) | Invalid for Clearance* |
| Consular Invoice | Govt. Certified | Post-production | Required in select nations (e.g. LATAM) |
*Note: Some countries may accept Proforma Invoices for Import Licenses, but rarely for final clearance.
3. Mandatory Compliance Fields
To ensure "Reasonable Care" standards are met, the following data points are non-negotiable:
A. Harmonized System (HS) Codes
The HS Code (or Tariff Schedule) determines the duty rate. The first 6 digits are the global standard established by the WCO.
- Digits 1-6: Universal Standard (Must be accurate).
- Digits 7-10: Country-specific statistical suffixes.
Visit WCO Official Site for updates on nomenclature changes.
B. Precise Goods Description
Vague descriptions are the leading cause of inspections.
Non-Compliant: "Machine Parts".
Compliant: "Hydraulic Seal Kit for Excavator, made of vulcanized rubber".
C. Country of Origin (COO)
This designates the economic nationality of the good (Manufacturing location), not the point of shipment. This is critical for applying Preferential Trade Agreements (e.g., USMCA, EU-UK TCA).
4. Risk Assessment: Penalties & Delays
Failure to provide an accurate Commercial Invoice constitutes a violation of customs laws.
Declaring a value lower than the transaction price is considered fraud. Authorities have access to global pricing databases to flag anomalies.
Using the wrong term (e.g., DDP vs. DAP) can force the seller to pay unexpected import VAT and duties, erasing profit margins.
In extreme cases of misdeclaration (especially regarding dual-use goods), shipments can be seized and destroyed.
5. Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
Follow this 5-step protocol to execute a compliant document.
- Step 1: Entity Identification (EOR/IOR)
Clearly distinguish between the Sold To (Buyer) and Ship To (Consignee) parties. Include Tax IDs (VAT/EORI/EIN) for both entities to facilitate tax assessment.
- Step 2: Define Terms of Trade
State the Incoterm® and the named place of destination (e.g., "CIP Heathrow Airport"). This defines the point where risk transfers.
- Step 3: Line Item Classification
For every item: Description, HS Code, Quantity, Unit of Measure, Unit Value, and Total Value. Warning: Ensure the currency (USD, EUR, CNY) is explicitly stated.
- Step 4: Origin & Weight Logic
Verify that the Net Weight + Packaging Weight = Gross Weight. Discrepancies in weight are a red flag for smuggling.
- Step 5: Legal Certification
The document must be signed (traditionally in blue ink) with the statement: "I hereby certify that the information on this invoice is true and correct..."
6. Digital Customs (ICS2, ACE, & ETD)
As of 2026, customs regimes have shifted towards Advance Cargo Information.
- EU ICS2: Requires detailed line-item data sent digitally prior to loading.
- US ACE: Automated Commercial Environment requires electronic data transmission.
- Paperless Trade (ETD): Most carriers (DHL, FedEx, UPS) allow the Commercial Invoice data to be transmitted electronically (PLT).
7. Annotated Document Specimen
The visual guide below highlights the critical data zones required by customs officers.
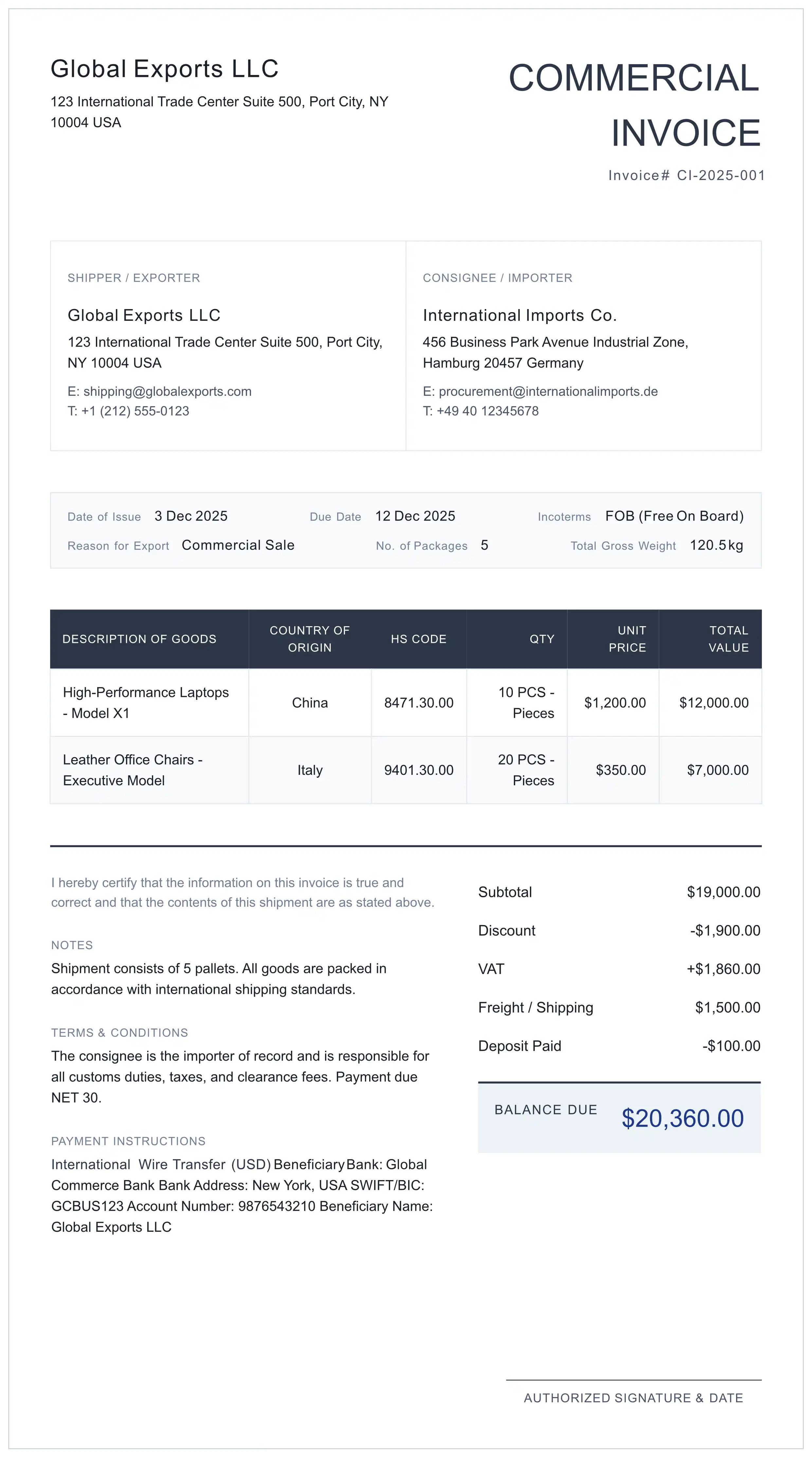
8. Technical FAQ
Does a Commercial Invoice serve as a proof of ownership?
No. The Commercial Invoice is a bill of sale that documents the transaction and declares the value of goods—but it does not transfer legal title (ownership). In international trade, the Bill of Lading is the primary document of title. The Commercial Invoice serves as proof of the sale, is used for customs clearance and duty calculation, and supports payment processing (e.g., Letters of Credit), but ownership transfer is governed by the sales contract and accompanying title documents.
Is a 'Zero Value' declaration acceptable for samples?
No. Customs authorities (including US CBP and EU Customs) do not accept zero-value declarations. Even for samples or gifts, a realistic market value ("Fair Market Value") must be declared for statistical and tax purposes, often marked as 'Value for Customs Purposes Only'.
What is the penalty for incorrect HS Code classification?
Incorrect classification can result in administrative fines, seizure of goods, and post-entry audits. It may also cause the loss of import privileges. Always cross-reference the first 6 digits with the WCO Harmonized System.
Can I use a handwritten Commercial Invoice?
While not explicitly illegal in all jurisdictions, handwritten invoices are strongly discouraged and often rejected by modern digital customs systems (like ACE or ATLAS) due to illegibility. A typed, standardized document is the global standard.
What is the difference between a Commercial Invoice and a Proforma Invoice?
A Commercial Invoice is the final bill of sale required for customs clearance, while a Proforma Invoice is a preliminary quote issued before the sale. Commercial Invoices are legally binding and mandatory for import/export; Proforma Invoices are non-binding estimates used for quotation and pre-shipment planning.
Do I need a Commercial Invoice for shipping with DHL, FedEx, or UPS?
Yes. All major shipping carriers (DHL, FedEx, UPS) require a Commercial Invoice for international shipments outside the EU. The invoice must include: Shipper/Receiver details, HS Codes, Country of Origin, declared value, and Incoterms. Most carriers allow electronic submission (Paperless Trade).
Legal Disclaimer & Liability Limitation
Informational Purposes Only: The contents of this "Commercial Invoice Protocol" are intended for general educational and reference purposes only. International trade regulations, including HS Codes, duty rates, and customs procedures, are subject to frequent changes by government entities (WCO, CBP, European Commission, HMRC). Information presented here may not reflect the most current legal developments or regulations applicable to your specific situation.
No Professional Advice: This document does not constitute legal, tax, customs brokerage, or any other professional advice. MyInvoiceTemplate and its editorial team are not licensed customs brokers, attorneys, or tax professionals. We expressly disclaim any and all liability for penalties, seizure of goods, delays, fines, or financial losses resulting from reliance on this guide or associated tools.
User Responsibility: Users are solely responsible for verifying the accuracy of information before acting upon it. You should always consult with a licensed Customs Broker, Trade Attorney, or qualified professional for advice specific to your shipments and compliance obligations. By using this resource, you acknowledge that any decisions made based on this information are made at your own risk.