Quick Answer: Invoice vs Receipt
"Please pay $500 by January 15th"
"Thank you! We received $500 on January 10th"
Need to create an invoice? Use our free invoice generator
Visual Comparison: Invoice vs Receipt
Before examining the legal code, visualize the transaction flow. The primary distinction is Timing relative to the payment event.
INVOICE
"Obligation to Pay"
- Timing: Before Payment
- Account: Accounts Receivable
- Action: Requires Settlement
RECEIPT
"Confirmation of Payment"
- Timing: After Payment
- Account: Cash / Bank
- Action: File for Audit
When to Use an Invoice vs Receipt
📄 Use an Invoice When...
- You've completed work but haven't been paid yet
- You're sending a payment request to a client
- You need to track accounts receivable
- You're billing for services or products
- You need to claim VAT/GST on the transaction
🧾 Use a Receipt When...
- You've received payment and need to confirm it
- A customer asks for proof of purchase
- You need documentation for tax deductions
- You're closing out an accounts receivable entry
- Recording a cash sale at point of purchase
Learn more: How to create a professional invoice
Real-World Examples
🎨 Freelancer Example
Designer completes logo project
Sends INVOICE: "Pay $500 in 30 days"
Client pays via bank transfer
Sends RECEIPT: "$500 received"
Freelancers: Create your free freelance invoice
🛒 Retail Example
Customer buys coffee → Gets RECEIPT immediately (no invoice needed at point of sale)
🏢 B2B Example
Company A orders from Company B → B ships with INVOICE → A pays in 30 days → B sends RECEIPT
Key Differences: Invoice vs Receipt
A side-by-side comparison of the essential differences between invoices and receipts.
| Feature | Invoice | Receipt |
|---|---|---|
| Legal Function | Commercial Instrument (Demand for Payment) | Proof of Satisfaction (Discharge of Debt) |
| Transaction Timing | Issued **Pre-Payment** (Accrual Basis) | Issued **Post-Payment** (Cash Basis) |
| Accounting Impact | Increases Accounts Receivable (Asset) | Increases Cash / Reduces Receivable |
| Tax Point (Time of Supply) | Triggers VAT/Sales Tax Liability (Usually) | Confirms Tax Collection Date |
| Digital Format (2026) | Structured Data (XML/JSON) or PDF | Payment Gateway Confirmation / Email |
| Key Mandatory Field | Payment Terms (e.g., Net 30) | Payment Method (e.g., Visa *1234) |
For Accountants: Technical Details
Expand below for legal definitions, GAAP-aligned accounting principles, and audit compliance information.
📚 Legal Definitions (2026 Standards)
In the eyes of tax authorities like the IRS (USA) or HMRC (UK), these documents serve fundamentally different legal purposes.
1. The Invoice: A Commercial Instrument
An invoice is not merely a list of products; it is a legal request for payment. In B2B transactions, a valid tax invoice allows the buyer to reclaim VAT/GST. It transfers the ownership of goods (in many jurisdictions) or signifies the completion of a service, creating a liability on the buyer's part.
2. The Receipt: Evidence of Discharge
A receipt is a written acknowledgment that value has been transferred. Legally, it acts as a discharge of debt. It proves that the obligation created by the invoice has been satisfied.
📊 GAAP Journal Entries
For professional bookkeepers and accountants, the difference is defined by how the transaction is recorded in the General Ledger. Below are the standard Double-Entry Bookkeeping standards.
Scenario A: Issuing an Invoice
You have completed the work, but haven't received cash yet (Accrual Basis).
Scenario B: Issuing a Receipt
The client sends the money. You confirm receipt.
Note: If you operate on a Cash Basis (common for very small businesses), the Invoice is a memo only, and Revenue is only recorded when the Receipt is generated.
✅ Audit Compliance & 3-Way Matching
In 2026, keeping paper records is becoming obsolete and, in some regions, non-compliant. Digital audit trails are the standard.
The 3-Way Matching Rule
For robust internal controls, large companies perform "3-Way Matching" before releasing funds. Your documentation must align with this process:
- Purchase Order (PO): What was ordered.
- Receiving Report (or Packing Slip): What was delivered.
- Invoice: What is being charged.
The Receipt comes after this cycle to close the book. If your invoice implies items not on the PO, or if your receipt dates do not align with bank statements, you risk failing a tax audit.
The "Paid Invoice" Protocol
Can a single document serve both purposes? Yes, under specific conditions. This is often called a "Commercial Invoice and Receipt" combined document.
To convert an Invoice into a valid Receipt legally:
- It must clearly state the original Invoice Reference Number.
- It must be marked with a permanent stamp or digital watermark stating "PAID".
- It must show the Balance Due as 0.00.
- It must list the payment date and method.
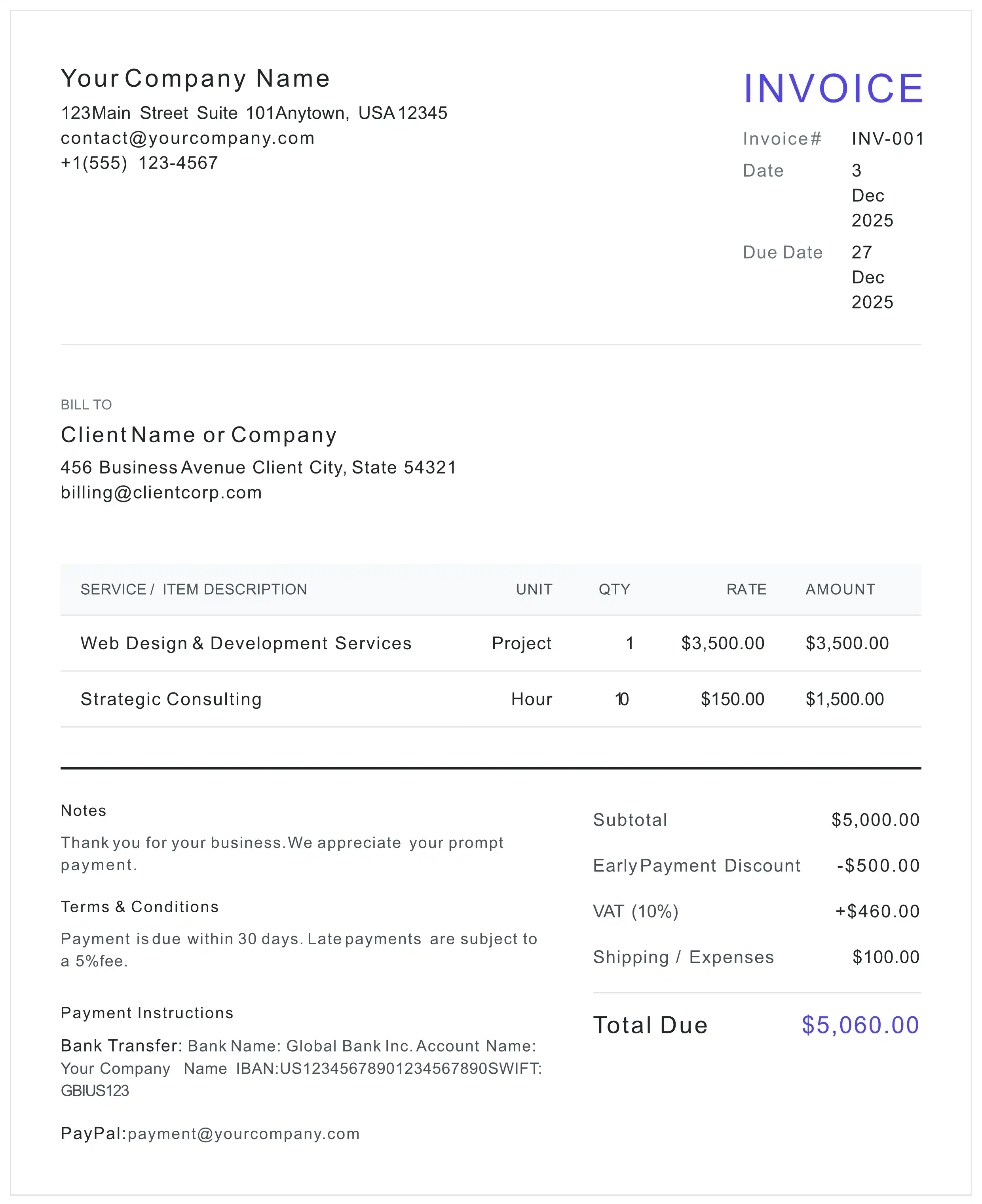
Execution Guide: Creating Valid Documents
Creating a Tax Invoice
- Legal Entity Identification
Ensure full legal names and tax IDs (VAT/EIN) of both seller and buyer are present.
- Sequential Control Number
Use a unique, gapless sequence (e.g., INV-2026-001) to satisfy audit requirements.
- Detailed Line Items
Description, quantity, unit price, and net amount must be explicit.
- Terms of Trade
Define the 'Net' days and Incoterms if applicable.
Creating a Payment Receipt
- Link to Origin
Reference the original Invoice Number to close the audit loop.
- Date of Settlement
The exact date funds cleared or were received.
- Mode of Payment
Specify Cash, Wire, Check, or Credit Card to aid reconciliation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a credit card slip considered a valid receipt for tax audits?
For small expenses, often yes. However, for significant business expenses and VAT deductions, tax authorities (like the IRS or HMRC) typically require an itemized receipt or invoice that shows the description of goods and tax breakdown, not just the total amount paid.
What is the difference between a Proforma Invoice and a Commercial Invoice?
A Commercial Invoice is a legal demand for payment that impacts your accounting books. A Proforma Invoice is a preliminary bill of sale sent to buyers in advance of a shipment or delivery of goods. A Proforma invoice is a 'quote' in invoice format and should NOT be recorded as an account receivable.
Do I need to issue a receipt if the client paid via bank transfer?
While the bank record acts as third-party proof, best practice dictates issuing a receipt or a 'Paid Invoice' confirmation. This ensures your client has a complete audit trail matching their own accounts payable records.
How do accrual vs. cash accounting affect these documents?
Under Accrual Accounting, you record income when the Invoice is sent (Revenue). Under Cash Accounting, you record income only when the Receipt is issued (Cash Received). Most growing businesses must use the Accrual method.
Can an invoice be used as a receipt?
Yes, but only if the invoice is marked as 'PAID' with zero balance, includes payment date/method, and references the original invoice number. This 'Paid Invoice' serves as a receipt.
Do I need both an invoice and receipt for taxes?
For business expenses, you need proof of what you paid for (invoice) and proof that you paid (receipt/bank statement). Keeping both creates a complete audit trail.
What is the difference between a bill and an invoice?
They're often used interchangeably. Technically, an invoice is what you SEND to request payment, a bill is what you RECEIVE asking you to pay. Same document, different perspective.
Is a paid invoice the same as a receipt?
A paid invoice can serve as a receipt if it shows: original invoice details, 'PAID' status, payment date, payment method, and zero balance due.
The information provided in this guide is intended for general educational and informational purposes only. While we strive to align content with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) as of 2026, tax laws and regulations vary significantly by jurisdiction (e.g., state sales tax nexus in the US, VAT rules in the EU, GST requirements in Australia and Canada).
This content does not constitute professional legal, accounting, financial, or tax advice. MyInvoiceTemplate and its contributors shall not be held liable for any decisions made or actions taken based on the information presented herein. For advice specific to your business circumstances, jurisdiction, or individual situation, please consult with a qualified professional such as a certified CPA (Certified Public Accountant), Chartered Accountant (CA), licensed Tax Attorney, or other appropriately credentialed advisor in your jurisdiction.