When to Issue a Credit Memo (6 Common Scenarios)
A credit memo should be issued whenever you need to reduce the amount a customer owes after an invoice has been finalized. Here are the most common scenarios:
1. Billing Errors & Overcharges
You accidentally charged $1,200 instead of $1,000. Issue a credit memo for $200 to correct the overcharge.
2. Product Returns (RMA)
Customer returns defective goods. Issue a credit memo to reduce their balance and update inventory.
3. Service Level Failures
You didn't meet the SLA (99.9% uptime, but delivered 98%). Issue a credit memo for the agreed penalty.
4. Post-Invoice Discounts
Customer qualifies for early payment discount after invoice was sent. Issue credit memo for discount amount.
5. Negotiated Price Reductions
After invoicing, you agree to a lower price. Issue a credit memo for the difference.
6. Duplicate Billing Corrections
You accidentally invoiced the same item twice. Issue a full credit memo for the duplicate.
Credit Memo vs Refund vs Debit Memo: What's the Difference?
These three terms often cause confusion. Here's a clear breakdown:
Swipe left/right to view full comparison
| Feature | Credit Memo | Cash Refund | Debit Memo |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduces customer's balance (no cash moves) | Returns cash to customer | Increases customer's balance (they owe more) |
| Cash Flow Impact | None - non-cash transaction | Cash outflow | None - non-cash transaction |
| Balance Sheet | Reduces Accounts Receivable | Reduces Cash | Increases Accounts Receivable |
| Common Use | B2B with payment terms (Net 30) | B2C or immediate settlements | Additional charges after invoice |
| Example | "We credited $200 to your account" | "We refunded $200 to your card" | "We added $50 shipping to your invoice" |
Decision Tree: Which Document Should You Use?
Q: Has the customer already paid?
Q: Do you need to reduce or increase their balance?
Journal Entry Examples: How to Record a Credit Memo
Proper accounting requires adjustments on both the Seller's and the Buyer's ledger. Below are the standard double-entry records.
A. Seller's Perspective (Issuing the Credit)
Scenario: Crediting a $100 Service + $10 Tax
Swipe to view entries
| Account Name | Account Type | Debit (Dr) | Credit (Cr) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales Returns & Allowances | Contra Revenue | $100.00 | |
| Sales Tax / VAT Payable | Liability | $10.00 | |
| Accounts Receivable | Asset | $110.00 |
B. Buyer's Perspective (Receiving the Credit)
The counterparty must record a "Debit Memo" entry to reduce their liability.
Swipe to view entries
| Account Name | Account Type | Debit (Dr) | Credit (Cr) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accounts Payable | Liability | $110.00 | |
| Purchase Returns / Inventory | Contra Expense / Asset | $100.00 | |
| Input VAT (Tax Receivable) | Asset | $10.00 |
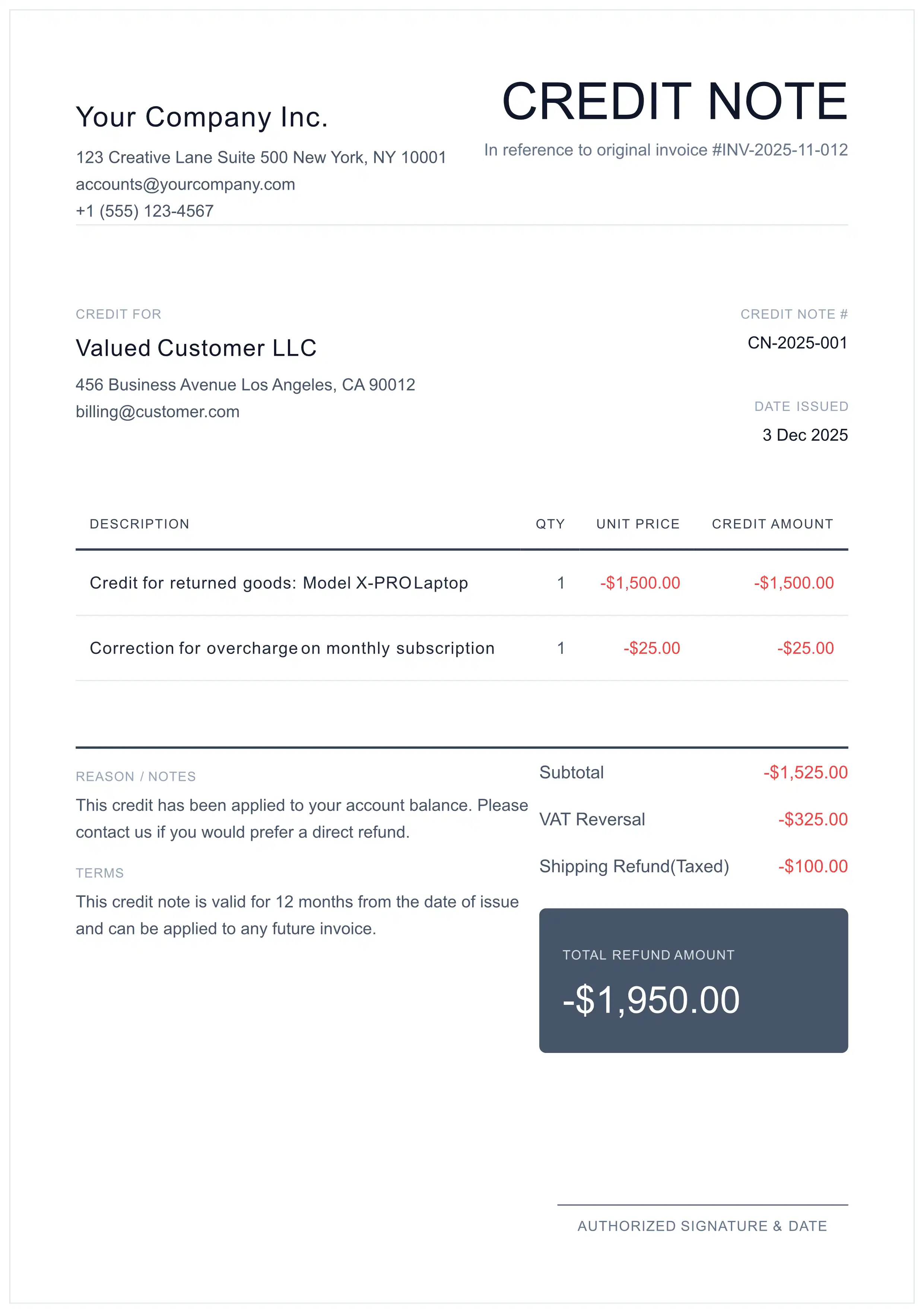
How to Create a Credit Memo (Step-by-Step)
To ensure acceptance by Accounts Payable departments and auditors, follow these steps when creating a credit memo:
 1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 Reference the Original Invoice
Always include: "Credit applied against Invoice #INV-2026-001". This creates the audit trail and prevents "orphan credits" in your ledger.
Use Sequential Numbering
Create a unique ID separate from invoices (e.g., CN-2026-001). Never reuse or modify invoice numbers.
List the Credited Items
Specify exactly which line items are being credited and why. Include the tax adjustment for each item.
Send Immediately
Distribute the credit memo to the customer promptly. They need it to adjust their Accounts Payable records.
Ready to create your credit memo?
Generate Free Credit Memo PDFCommon Credit Memo Mistakes to Avoid
Deleting the Original Invoice
Problem: Breaks audit trail, may be flagged as fraud.
Solution: Always issue a credit memo instead of deleting.
Wrong Numbering Sequence
Problem: Using invoice numbers for credit memos causes confusion.
Solution: Use separate sequence (CN-2026-001, CN-2026-002).
Missing Original Invoice Reference
Problem: Auditors can't trace the correction.
Solution: Always include "Credit against Invoice #INV-XXX".
Tax Calculation Errors
Problem: Crediting wrong tax amount causes VAT/GST issues.
Solution: Calculate tax reversal on the credited line items only.
For Accountants: Technical Details
Expand below for GAAP/IFRS-aligned accounting principles and compliance requirements.
📚 Legal Definition & Compliance Standards
A Credit Memo (Credit Note) is a legally binding "Source Document" in accounting that authorizes a reduction in the amount a buyer owes to a seller. Unlike a simple discount, it is a formal acknowledgment of debt reduction after an invoice has been finalized.
To maintain a clean audit trail, organizations must adhere to strict issuance protocols. Arbitrary issuance of credit notes can trigger audits by bodies such as the IRS or HMRC.
📊 IAS 10: Events After Reporting Period
🌍 Tax Statutes by Jurisdiction (US, UK, EU)
| Jurisdiction | Authority | Statute of Limitations (Reclamation) |
|---|---|---|
| United States | IRS | 3 Years (from return filing) |
| United Kingdom | HMRC | 4 Years (from end of accounting period) |
| European Union | EU Council | Subject to National Laws (Min 1 Year) |
📋 Credit Memo Workflow Best Practices
Follow this recommended workflow when utilizing our Credit Note Generator to ensure process uniformity and compliance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a credit memo in simple terms?
A credit memo is a document that reduces the amount a customer owes to a seller. It's issued when an invoice needs to be corrected - for example, if you overcharged a customer, they returned goods, or you agreed to a discount after sending the invoice.
Can I delete an invoice instead of issuing a credit memo?
No - strictly prohibited. Deleting a finalized invoice breaks the audit trail and may be flagged as fraud. Always issue a credit memo to maintain legal compliance.
What's the difference between a credit memo and a refund?
A credit memo reduces the customer's balance (no cash moves). A refund returns actual cash to the customer. Use credit memos for B2B transactions with payment terms; use refunds when the customer has already paid.
What information must a credit memo contain?
A valid credit memo must include: (1) 'Credit Memo' or 'Credit Note' title, (2) unique sequential number, (3) reference to original invoice, (4) issue date, (5) credited line items with amounts, (6) tax adjustment if applicable, (7) total credit amount.
How do I record a credit memo in accounting?
For sellers: Debit 'Sales Returns & Allowances' (contra-revenue) and 'Sales Tax Payable', Credit 'Accounts Receivable'. For buyers: Debit 'Accounts Payable', Credit 'Purchase Returns' and 'Input VAT'.
Is a credit memo the same as a credit note?
Yes, they're the same document. 'Credit Memo' is the US term (GAAP), while 'Credit Note' is used in UK, EU, and Australia (IFRS). Both reduce the amount a customer owes.
When should I issue a credit memo vs. a new invoice?
Issue a credit memo to correct an existing invoice (errors, returns, discounts). Issue a new invoice only for completely new transactions or when the original invoice hasn't been finalized yet.
How does a credit memo affect revenue recognition?
A credit memo is a contra-revenue adjustment under ASC 606/IFRS 15. It reduces 'Gross Sales' to 'Net Sales' on the income statement - it's a reversal of recognized revenue, not an expense.
Legal & Financial Disclaimer
Institutional Reference Only: This document is a technical reference for informational purposes, maintained by MyInvoiceTemplate.com under our Corporate Governance standards. While verified against 2026 GAAP/IFRS standards, it does not replace the advice of a certified tax professional in your specific jurisdiction. Accounting regulations are subject to change. Please consult your internal finance controller or external auditor before applying significant General Ledger adjustments.