Compliance Notice: This guide references WTO Valuation Rules, ICC Incoterms® 2020, and EU CBAM Regulations. Customs regulations change frequently. This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute legal or professional advice. Always verify current requirements with official sources.
In the era of automated customs clearance, the Commercial Invoice is no longer just a request for payment—it is a mandatory data declaration. Customs authorities (CBP, HMRC, EU Customs) now utilize AI-driven risk assessment to audit invoices before the cargo even leaves the origin country. This protocol outlines the strict requirements to ensure clearance, prevent fiscal penalties, and maintain trade compliance in 2026.
International Invoice vs Commercial Invoice vs Proforma
Understanding the differences between these document types is critical for customs compliance. Customs authorities require the definitive "Bill of Sale" (Commercial Invoice) for duty assessment.
| Document Type | Purpose | When to Use | Legal Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proforma Invoice | Pre-shipment quote / Import license application | Before sale is confirmed | NOT legally binding |
| Commercial Invoice | Customs clearance, duty assessment | With every international shipment | Legally binding declaration |
| International Invoice | Same as commercial invoice (used interchangeably) | Cross-border B2B transactions | Legally binding declaration |
For a detailed comparison, see our Proforma Invoice Guide.
Required Fields for a Compliant International Invoice
A valid international invoice must act as a complete data source. Omissions in the "Sold To" or "Ship To" fields are the primary cause of clearance holds in the US ACE (Automated Commercial Environment) system.
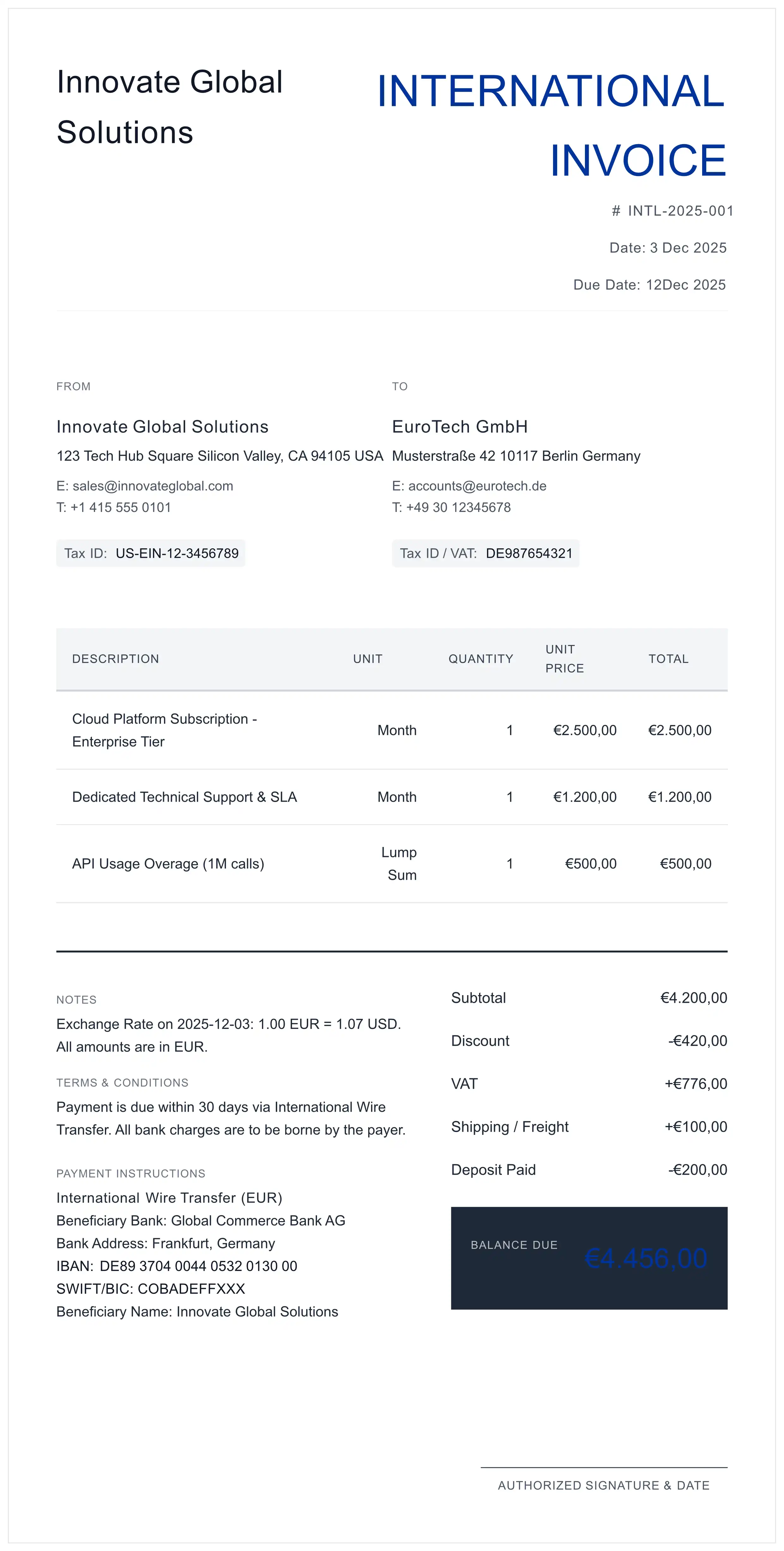
A. Entity Identification (KYC)
- Exporter (Seller): Full legal name and Tax ID.
- Importer of Record (Sold To): The entity responsible for duties. Mandatory: Include their Tax ID (VAT, EORI in Europe, EIN/IRS in USA).
- Consignee (Ship To): The final delivery location. Crucial for security screening.
B. Logistics & References
- Invoice Number: Must be unique and sequential for audit trails.
- Waybill (AWB/BOL): The carrier's tracking number, linking the physical cargo to this document.
- Country of Origin: The country of manufacture (not shipment). This determines tariff rates and sanctions.
Customs Compliance: HS Codes & Incoterms 2020
This section covers the technical classification and terms of trade defined by international bodies.
Harmonized System (HS) Codes
The World Customs Organization (WCO) manages the HS system. You must assign a 6-digit code to every physical item.
Do not use general descriptions. A "Machine part" will be rejected. Use the specific HS Code definition. Verify via your local customs tariff schedule (e.g., US HTS or EU TARIC).
Preferential Origin
If your countries have a Free Trade Agreement (e.g., UK-EU TCA, USMCA), you must include a specific declaration statement on the invoice to claim 0% duty.
Incoterms® 2020 Rules
Published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC), these rules define costs and—crucially—Transfer of Risk.
| Incoterm® | Definition | Seller Responsibility | Buyer Responsibility | Risk Transfer Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXW | Ex Works | Minimal. Goods ready at factory. | Pick-up, Export/Import Customs. | At Seller's Warehouse. |
| FOB | Free on Board | Load on vessel/plane + Export Customs. | Freight, Insurance, Import. | When goods board the vessel. |
| DAP | Delivered at Place | Shipping to destination. | Import Duties & Unloading. | Ready for unloading at destination. |
| DDP | Delivered Duty Paid | Door-to-Door (inc. Duties). | Unloading only. | Ready for unloading at destination. |
Risk Matrix: International Invoice Errors & Penalties
Understanding the financial impact of invoicing errors is critical for 2026 compliance strategies.
| Error Type | Consequence | Estimated Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Incorrect HS Code | Duty miscalculation & Audit Trigger. | High: Penalties (2x-4x duty) + Delays. |
| Undervaluation | Seizure of goods for Fraud. | Critical: Loss of goods + Criminal charges. |
| Missing Origin | Denial of Preferential Duty (0%). | Medium: Unnecessary tax payments. |
| Sanctioned Party | Violation of OFAC/EU Laws. | Severe: Heavy fines & Frozen bank funds. |
The Customs Data Pipeline
Modern trade is a data flow. Documentation must be consistent across all steps to avoid "Data Mismatch" flags in systems like ACE or ATLAS.
1. Commercial Invoice
Data Source: Value, HS Codes, Origin, Incoterms.
2. Packing List
Physical Source: Net/Gross Weights, Dimensions.
3. AWB / Bill of Lading
Logistics Source: Carrier Contract & Tracking.
4. Customs Validation
AI Cross-Check: Invoice Data vs. X-Ray & Manifest.
How to Create an International Invoice: Step-by-Step
- Template Selection: Use a compliant Commercial Invoice format. Ensure it supports "Multi-line items" for detailed HS coding.
- Deep Classification: Assign HS Codes to the 6th digit. Verify if the destination requires 8 or 10 digits (e.g., Schedule B for US Exports).
- Valuation Strategy: Declare the "True Transaction Value". Do not undervalue goods to save on taxes; this is considered fraud. Even samples must have a nominal value for customs purposes (e.g., $1.00 - "Value for Customs Only").
- Specific Descriptions: Replace generic terms. Instead of "Clothes", write "Men's Cotton T-Shirt, Knitted".
- Certification: The invoice must be signed by an authorized signatory stating: "I declare that the information contained in this invoice is true and correct."
Country-Specific Customs Requirements
Each country has specific requirements for international invoices. Here are the essentials for major markets:
United States (CBP)
- System: ACE (Automated Commercial Environment)
- Required: 10-digit HTS code, EIN/SSN, Country of Origin
- Threshold: Formal entry for goods over $2,500
- De Minimis: $800 exemption suspended (Aug 2025)
- Ocean: ISF (10+2) filing required 24hrs before loading
European Union
- System: ICS2 / ATLAS (varies by country)
- Required: EORI number, VAT ID, 8-digit CN code
- ViDA: Cross-border B2B e-invoicing mandatory from July 2030
- CBAM: Carbon reporting for steel/aluminum/cement/fertilizers/hydrogen
United Kingdom (HMRC)
- System: CDS (Customs Declaration Service) - CHIEF retired in 2024
- Required: EORI number (GB prefix + 12 digits), Commodity code
- Post-Brexit: Full customs declarations required for all EU trade
- VAT: Postponed VAT accounting available
Canada (CBSA)
- System: CARM (Assessment and Revenue Management)
- Required: Business number, HS code, CUSMA origin
- Threshold: Formal entry for goods over CAD $3,300
- FTA: CUSMA Certificate of Origin for duty-free
Australia (ABF)
- System: ICS (Integrated Cargo System)
- Required: ABN, Working tariff code, Country of Origin
- GST: 10% GST on imports over AUD $1,000
- Biosecurity: Additional declarations for food/plants
China (GACC)
- System: Single Window Platform (CIFER)
- Required: 10-digit HS code, GACC registration (18-digit number)
- Food Exports: Decree 248/249 registration for food manufacturers
- Language: Chinese translation may be required
Common International Invoicing Mistakes to Avoid
These errors cause customs delays, penalties, and lost shipments:
Undervaluing Goods
Impact: Fraud investigation, goods seizure, criminal charges.
Solution: Declare true transaction value including shipping/insurance where applicable (per Incoterms).
Wrong or Missing Country of Origin
Impact: Loss of preferential duty rates (FTA benefits), tariff evasion flags.
Solution: State manufacturing country (not shipping origin). Include origin certificates for FTA claims.
Generic Product Descriptions
Impact: Automatic inspection triggers, clearance delays.
Solution: Use specific descriptions: "Men's Cotton T-Shirt, Knitted" not "Clothes".
Missing or Invalid Incoterms
Impact: Unclear liability, insurance disputes, payment issues.
Solution: Use official ICC Incoterms 2020 with named place (e.g., "DAP New York Terminal").
Digital Trade: ViDA, ACE & Peppol
We are transitioning from "Paperless" to "Structured Data".
- Electronic Trade Documents (ETD): Carriers like DHL, FedEx, and UPS transmit your Commercial Invoice data directly to customs via API.
- US ACE Portal: For exports to the USA, data quality is paramount. Incomplete invoices are rejected instantly by the Automated Commercial Environment. Note: The $800 de minimis exemption was suspended in August 2025.
- ViDA (VAT in the Digital Age): The EU adopted ViDA in March 2025. Cross-border B2B e-invoicing becomes mandatory from July 2030. Member states with existing domestic systems (Italy, France, Poland) must align by January 2035. PDF invoices may not meet compliance requirements.
CBAM & Carbon Reporting for Exporters
Under the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM), importers of Iron, Steel, Aluminum, Cement, Fertilizers, Electricity, and Hydrogen into the EU must report "Embedded Emissions". CBAM went live on January 1, 2026.
As an exporter, you must provide the Importer with:
- Net Weight of the specific CBAM goods.
- Direct Emissions: CO2e emitted during production.
- Indirect Emissions: CO2e from electricity used in production.
De Minimis Exemption: Importers bringing in 50 tonnes or less of CBAM goods annually are exempt (except electricity and hydrogen).
Penalties: Non-compliance results in €100 per tonne of CO2 equivalent (aligned with EU ETS). Unauthorized importers face 3-5x penalties.
Sanctions Screening & Banking Details
Denied Party Screening (Sanctions)
Before generating an invoice, you must ensure the "Sold To" and "Ship To" parties are not on any International Sanctions Lists (e.g., OFAC, UN, EU Consolidated List).
Banking Details
To ensure payment, include full banking coordinates:
- IBAN: International Bank Account Number (Standard for EMEA).
- SWIFT/BIC: Bank Identifier Code.
- Currency: Explicitly state the currency code (USD, EUR, GBP) to avoid exchange rate disputes.
Free International Invoice Template & Generator
Create a customs-compliant commercial invoice in minutes:
100% free. No signup. Instant PDF download.
Related Invoice Tools:
Statutory References
This protocol is built upon regulations from the following authoritative bodies:
- WTO: Agreement on Customs Valuation (Article VII of GATT)
- WCO: Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System (HS)
- ICC: Incoterms® 2020 Rules
- EU Commission: Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)
- US CBP: U.S. Customs and Border Protection - Basic Import and Export Requirements (visit cbp.gov)
International Invoicing FAQ
Is a PDF invoice accepted by US Customs (CBP) and EU Authorities?
For basic clearance, yes. However, under the US ACE (Automated Commercial Environment) and EU's ViDA proposals, structured data (XML/EDI) is becoming mandatory for rapid clearance. A simple PDF may trigger manual inspections (Intensive Exam), causing 24-72 hour delays.
How does the 'Exporter of Record' liability change in 2026?
Previously, brokers often took the blame. In 2026, customs authorities (like HMRC and CBP) hold the Exporter of Record 100% financially liable for HS Code errors, even if a third party created the invoice. Ignorance is no longer a legal defense.
What is the penalty for missing CBAM data on an invoice?
If you export Iron, Steel, Aluminum, Cement, Fertilizers, or Hydrogen to the EU, missing 'Embedded Emission' data prevents the importer from filing their declaration. From 2026, non-compliance results in a penalty of €100 per tonne of CO2 equivalent (aligned with EU ETS), plus the importer must still surrender the required CBAM certificates. Unauthorized importers face penalties up to 3-5 times this amount.
Do I need a signature on a digital commercial invoice?
Yes. While physical ink is less common, a Digital Signature or a statement certifying accuracy (e.g., 'I hereby certify...') is mandatory. It legally binds the entity to the declared values for tax purposes.
What is the difference between a commercial invoice and a proforma invoice?
A proforma invoice is a preliminary quote sent before goods are shipped—it's not legally binding. A commercial invoice is the official document used for customs clearance and is legally binding. Customs authorities require the commercial invoice for duty assessment.
How do I find the correct HS Code for my product?
Use official tariff databases: US HTS (hts.usitc.gov), EU TARIC (ec.europa.eu), or your country's customs authority. Start with the 6-digit WCO code, then add country-specific digits (8-10 digits for US/EU).
Which Incoterm should I use for international shipping?
It depends on your agreement: FOB (buyer arranges shipping from port), DAP (seller delivers to destination, buyer pays duties), DDP (seller handles everything including duties). Always specify the named place (e.g., 'DAP New York Terminal').
Do I need a commercial invoice for samples or gifts?
Yes. Even samples and gifts require a commercial invoice for customs. Declare nominal value (e.g., '$1.00 - Value for Customs Only') and mark as 'Sample - Not for Resale' or 'Gift - No Commercial Value'.
Legal Disclaimer: The information provided on this page is for general educational and informational purposes only regarding international trade standards. It does not constitute, and should not be relied upon as, legal, customs, tax, or professional advice. Trade regulations, sanctions, tariffs, and compliance requirements (including CBAM, ViDA, HS codes) are subject to frequent changes by national and international authorities. We make no warranties or representations about the accuracy, completeness, or currentness of this information. For specific guidance on your shipments, always consult a licensed customs broker, trade compliance specialist, or qualified legal professional in the relevant jurisdiction. Use of this information is at your own risk. MyInvoiceTemplate and its affiliates disclaim all liability for any losses, damages, or penalties arising from reliance on this content.