1. When Do You Need a Proforma Invoice?
A Proforma Invoice is essential in specific international trade scenarios. Here are the 5 most common use cases:
1. Letter of Credit (L/C) Applications
Banks require a Proforma Invoice to open an L/C under UCP 600 rules. The document establishes the terms of sale before funds are committed.
2. Customs Clearance & Import Licenses
Customs authorities use the Proforma to issue import permits and assess potential duties before goods arrive at the destination port.
3. Sample & "No Commercial Value" Shipments
When sending product samples or prototypes with no sale value, a Proforma Invoice with "No Commercial Value" declaration is required for customs.
4. Budget Approval & Planning
Purchasing departments use Proforma Invoices to secure internal budget approvals before committing to a purchase order.
5. Price Quotations for International Trade
Unlike informal quotes, a Proforma Invoice provides a formal price commitment with specific validity periods, protecting both parties.
2. Legal Definition & Purpose
A Proforma Invoice constitutes a preliminary bill of sale in international trade. Legally, it functions as a non-binding "Offer to Sell" under the principles of commercial contract law, specifically structured to assist the buyer in securing financing, import licenses, or opening a Letter of Credit (L/C).
Unlike a Commercial Invoice, a Proforma Invoice is not a fiscal demand for payment and should not be entered into the seller's Accounts Receivable ledger. However, once countersigned by the buyer, it can serve as a legally binding sales contract, subject to the terms (Incoterms) specified therein.
3. Regulatory Compliance (UCP 600 & Customs)
In the context of 2026 global trade standards, the Proforma Invoice serves two critical regulatory functions. Failure to adhere to these standards often results in shipment demurrage charges and banking discrepancies.
A. Letter of Credit (L/C) and UCP 600
For transactions financed via Letter of Credit, the Proforma Invoice is the foundational document. Banks operate under the Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (UCP 600). The bank will issue the L/C based strictly on the data provided in the Proforma.
- Description Consistency: The description of goods in the Proforma must match the eventual Commercial Invoice character for character.
- Beneficiary Details: The seller's name must match the bank account beneficiary exactly to prevent AML (Anti-Money Laundering) flags.
- Validity Period: The L/C must be opened before the Proforma's "Validity Date" expires.
B. Customs Valuation & Licensing
Import authorities require the Proforma to issue an Import License. The declared value in the Proforma sets the baseline for the "Customs Value." Undervaluation at this stage can lead to fines under global transfer pricing regulations.
4. Incoterms & Logistics Variables
A valid Proforma Invoice must define the "Transfer of Risk" and "Transfer of Cost." This is achieved through Incoterms® (International Commercial Terms). The selected term directly impacts the final price shown on the invoice.
| Term | Full Name | Seller's Responsibility | Impact on Proforma Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| EXW | Ex Works | Goods made available at factory. | Lowest Price (Product cost only). |
| FOB | Free on Board | Loaded onto the vessel. | Product + Inland Freight + Port Handling. |
| CIF | Cost, Insurance & Freight | Delivery to destination port + Insurance. | Product + Freight + Insurance Premium. |
| DDP | Delivered Duty Paid | Door-to-door delivery including Taxes. | Highest Price (Includes Duties & VAT). |
Note: The Proforma must clearly state the Incoterm version (e.g., "CIF New York, Incoterms® 2020") to avoid legal ambiguity.
5. Proforma vs Commercial Invoice vs Quotation
Distinct documentation phases require distinct instruments. Mixing these documents disrupts the audit trail and tax reporting.
| Attribute | Proforma Invoice | Commercial Invoice | Quotation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accounting Status | Off-Balance-Sheet (No Journal Entry) | Accounts Receivable (Tax Event) | None |
| Primary Function | Customs Clearance / Financing (L/C) | Payment Demand / Title Transfer | Price Proposal |
| Changeability | Negotiable (Can be amended) | Final (Credit Note required to change) | Fluid |
| Banking | Required for L/C Issuance | Required for Fund Release | Not Accepted |
6. Mandatory Data Fields
To ensure cross-border validity and minimize customs holds, modern Proforma Invoices must contain specific data vectors. Our free generator helps you include these fields automatically.
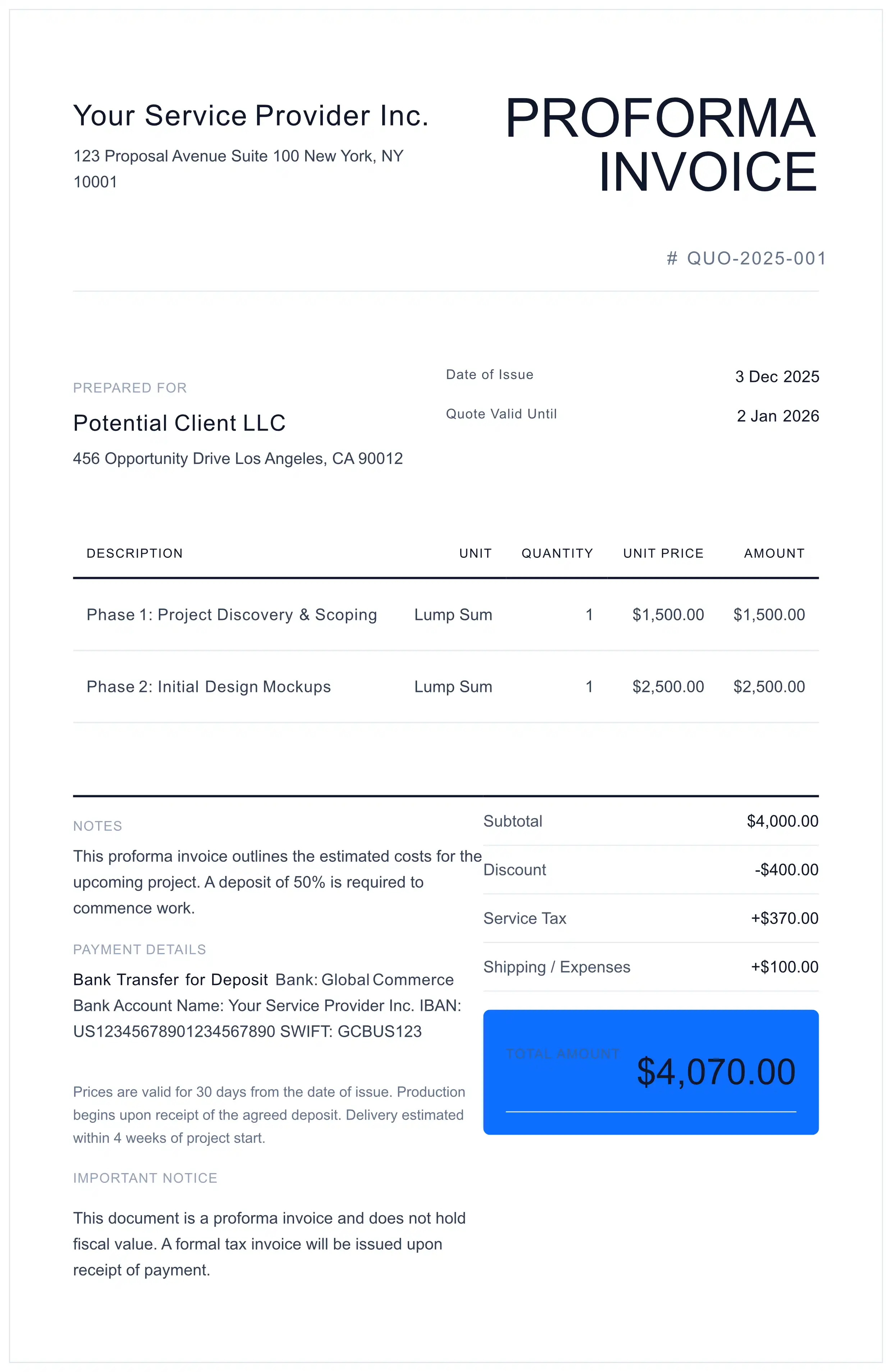
Critical Data Points
- HS Codes (Harmonized System): The 6-to-10 digit code classifying the product. Essential for determining tariff rates.
- Country of Origin: Mandatory for preferential duty treaties (e.g., USMCA, EU Trade Agreements).
- Weight & Dimensions: Net Weight (NW) and Gross Weight (GW) are required for freight calculation and customs manifesting.
- Currency & Exchange Rate: Clearly state the currency (USD, EUR, GBP) to avoid foreign exchange (FX) disputes.
- Validity Date: A strict deadline (e.g., "Valid for 30 days") to protect the seller from raw material price volatility.
7. How to Create a Proforma Invoice (5 Steps)
Follow these steps to create a compliant Proforma Invoice that meets international trade standards. Use our free generator tool to automate this process.
Verify Compliance Requirements
Check the destination country's specific import regulations. Determine if special licenses, certificates, or declarations are required for your product category.
Assign HS Codes
Classify your products using the correct 6-to-10 digit Harmonized System (HS) codes. Incorrect classification can result in customs delays and penalties.
Define Incoterms
Specify the transfer of risk and cost using Incoterms 2020 definitions (EXW, FOB, CIF, DDP). This determines who pays for shipping, insurance, and duties.
Set Validity Period
Insert a mandatory expiration date (e.g., "Valid for 30 days") to protect against currency fluctuations and raw material price changes.
Generate & Send
Create the secure PDF document and transmit it to the buyer for L/C issuance or customs pre-clearance. Keep a copy for your records.
8. Risk Management: Manual vs. Automated
The use of static spreadsheet templates (Excel/Word) for Proforma Invoicing introduces significant operational risk. In a modern "Digital Customs" environment, data integrity is paramount.
The Risk of Static Templates
Manual entry errors in HS Codes or calculation formulas often result in Customs Audits and shipment rejection. Furthermore, Excel templates lack the audit trail required by ISO 9001 standards.
The Automated Advantage
Using a dedicated generator ensures that mandatory disclaimers (e.g., "This is not a VAT invoice") and validity dates are programmatically enforced. It also allows for the seamless conversion to a Commercial Invoice without data re-entry, preserving data integrity.
Ready for Shipment?
Once the Proforma is accepted and goods are dispatched, you must issue the Commercial Invoice to trigger the legal transfer of ownership and payment.
9. Frequently Asked Questions
Does a Proforma Invoice constitute a legally binding contract?
Can Proforma Invoices be used for Customs Valuation?
What is the role of a Proforma in a Letter of Credit (L/C)?
Should Proforma Invoices be recorded in General Ledger (GL)?
What is the difference between a Proforma Invoice and a Commercial Invoice?
How do I create a Proforma Invoice for free?
Legal & Financial Disclaimer
Information Only: The content provided in this guide is for general educational and informational purposes only. It does not constitute legal counsel, tax advice, accounting guidance, or binding customs consultancy. MyInvoiceTemplate assumes no liability for any actions taken based on this information.
Variation by Jurisdiction: Trade regulations (VAT rules, Customs Duties, Embargoes, and import/export requirements) vary significantly by country and are subject to change without notice. Professional Verification: We strongly recommend consulting with a certified Customs Broker, Licensed CPA, or International Trade Attorney before executing cross-border transactions.
